relay comparison: exploring different types and their applications
Release time:2025-04-17 08:06:04
In the world of electrical engineering, relays are crucial components used to control circuits and protect electrical systems. These electromagnetic devices enable the switching of high voltage or high current circuits with the help of a low voltage or current signal. They are widely used in various applications, ranging from industrial machinery to automotive systems. Understanding the different types of relays and their respective advantages is essential for engineers and technicians in selecting the right relay for specific needs. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of various relay types, including electromagnetic relays, solid-state relays, and reed relays, to help readers make informed decisions in relay selection.
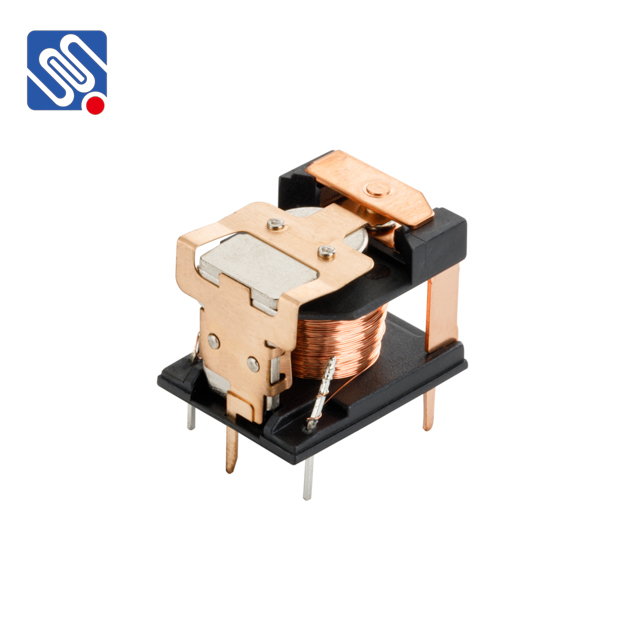
1. Electromagnetic Relays (Mechanical Relays)
Electromagnetic relays, often referred to as mechanical relays, are the most traditional and widely used type of relay. They operate by using an electromagnet to physically move a set of contacts, thus opening or closing a circuit. When a current flows through the coil of the relay, it creates a magnetic field that pulls a metal armature, activating the relay's contacts.
Advantages:
Cost-Effective: Electromagnetic relays are relatively inexpensive, making them a popular choice for many applications.
Versatile: These relays can handle a wide range of currents and voltages, from low to high power circuits.


